When Using Ipsec, How Can You Ensure That Each Computer Uses Its Own Private Key Pair?
What is IPsec (Cyberspace Protocol Security)?
IPsec (Net Protocol Security) is a suite of protocols and algorithms for securing data transmitted over the net or any public network. The Internet Engineering Task Force, or IETF, developed the IPsec protocols in the mid-1990s to provide security at the IP layer through hallmark and encryption of IP network packets.
IPsec originally divers ii protocols for securing IP packets: Authentication Header (AH) and Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP). The quondam provides data integrity and anti-replay services, and the latter encrypts and authenticates data.
The IPsec suite besides includes Internet Primal Exchange (IKE), which is used to generate shared security keys to establish a security association (SA). SAs are needed for the encryption and decryption processes to negotiate a security level between two entities. A special router or firewall that sits between 2 networks commonly handles the SA negotiation process.
What is IPsec used for?
IPsec is used for protecting sensitive data, such as financial transactions, medical records and corporate communications, as information technology's transmitted across the network. It's too used to secure virtual individual networks (VPNs), where IPsec tunneling encrypts all data sent between 2 endpoints. IPsec tin can too encrypt application layer data and provide security for routers sending routing data beyond the public internet. IPsec can also exist used to provide authentication without encryption -- for example, to authenticate that data originated from a known sender.
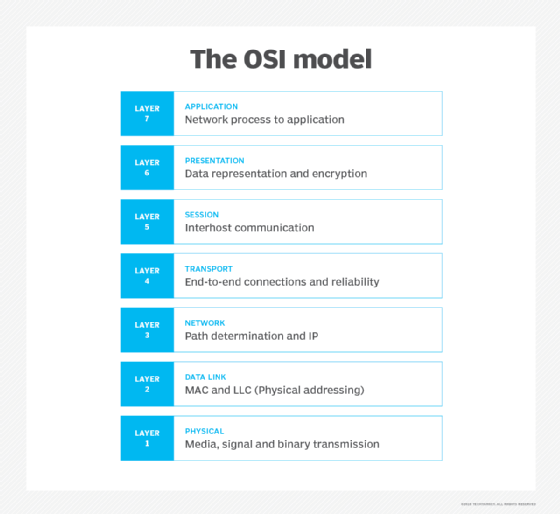
Encryption at the awarding or the transport layers of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model tin securely transmit data without using IPsec. At the application layer, Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) performs the encryption. While at the ship layer, the Send Layer Security (TLS) protocol provides the encryption. However, encrypting and authenticating at these higher layers increase the chance of data exposure and attackers intercepting protocol information.
IPsec protocols
IPsec authenticates and encrypts information packets sent over both IPv4- and IPv6-based networks. IPsec protocol headers are found in the IP header of a packet and define how the data in a package is handled, including its routing and delivery across a network. IPsec adds several components to the IP header, including security information and one or more cryptographic algorithms.
The IPsec protocols apply a format called Request for Comments (RFC) to develop the requirements for the network security standards. RFC standards are used throughout the cyberspace to provide important information that enables users and developers to create, manage and maintain the network.
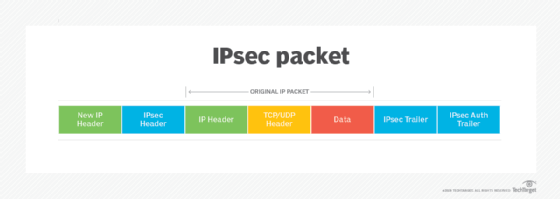
The following are primal IPsec protocols:
- IP AH. AH is specified in RFC 4302. It provides information integrity and transport protection services. AH was designed to be inserted into an IP packet to add together hallmark data and protect the contents from modification.
- IP ESP. Specified in RFC 4303, ESP provides hallmark, integrity and confidentiality through encryption of IP packets.
- IKE. Defined in RFC 7296, IKE is a protocol that enables two systems or devices to establish a secure advice aqueduct over an untrusted network. The protocol uses a serial of key exchanges to create a secure tunnel betwixt a client and a server through which they can send encrypted traffic. The security of the tunnel is based on the Diffie-Hellman cardinal exchange.
- Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP). ISAKMP is specified as part of the IKE protocol and RFC 7296. It is a framework for fundamental establishment, authentication and negotiation of an SA for a secure substitution of packets at the IP layer. In other words, ISAKMP defines the security parameters for how two systems, or hosts, communicate with each other. Each SA defines a connection in ane direction, from one host to another. The SA includes all attributes of the connection, including the cryptographic algorithm, the IPsec style, the encryption primal and any other parameters related to data transmission over the connection.
IPsec uses, or is used by, many other protocols, such every bit digital signature algorithms and most protocols outlined in the IPsec and IKE Document Roadmap, or RFC 6071.
How does IPsec work?
There are v key steps involved with how IPsec works. They are as follows:
- Host recognition. The IPsec process begins when a host system recognizes that a packet needs protection and should exist transmitted using IPsec policies. Such packets are considered "interesting traffic" for IPsec purposes, and they trigger the security policies. For outgoing packets, this means the appropriate encryption and authentication are applied. When an incoming packet is determined to be interesting, the host system verifies that information technology has been properly encrypted and authenticated.
- Negotiation, or IKE Phase i. In the 2d stride, the hosts apply IPsec to negotiate the set of policies they volition use for a secured circuit. They besides authenticate themselves to each other and set up a secure aqueduct between them that is used to negotiate the way the IPsec circuit volition encrypt or authenticate data sent across it. This negotiation process occurs using either main way or aggressive mode.
With principal mode, the host initiating the session sends proposals indicating its preferred encryption and hallmark algorithms. The negotiation continues until both hosts agree and fix an IKE SA that defines the IPsec excursion they will use. This method is more secure than aggressive fashion because it creates a secure tunnel for exchanging data.
In ambitious style, the initiating host does not allow for negotiation and specifies the IKE SA to exist used. The responding host's acceptance authenticates the session. With this method, the hosts can set up an IPsec circuit faster.
- IPsec excursion, or IKE Phase 2. Footstep iii sets up an IPsec circuit over the secure channel established in IKE Phase i. The IPsec hosts negotiate the algorithms that volition be used during the information transmission. The hosts too hold upon and exchange the encryption and decryption keys they plan to use for traffic to and from the protected network. The hosts also commutation cryptographic nonces, which are random numbers used to authenticate sessions.
- IPsec transmission. In the fourth step, the hosts exchange the actual information beyond the secure tunnel they've established. The IPsec SAs ready before are used to encrypt and decrypt the packets.
- IPsec termination. Finally, the IPsec tunnel is terminated. Usually, this happens subsequently a previously specified number of bytes have passed through the IPsec tunnel or the session times out. When either of those events happens, the hosts communicate, and termination occurs. After termination, the hosts dispose of the private keys used during data manual.
How is IPsec used in a VPN?
A VPN essentially is a private network implemented over a public network. Anyone who connects to the VPN can access this private network as if directly connected to it. VPNs are commonly used in businesses to enable employees to access their corporate network remotely.
IPsec is commonly used to secure VPNs. While a VPN creates a private network between a user'due south computer and the VPN server, IPsec protocols implement a secure network that protects VPN data from outside access. VPNs can be prepare using one of the two IPsec modes: tunnel mode and transport way.
What are the IPsec modes?
In simple terms, transport mode secures data as information technology travels from ane device to another, typically for a single session. Alternatively, tunnel mode secures the entire information path, from point A to point B, regardless of the devices in betwixt.
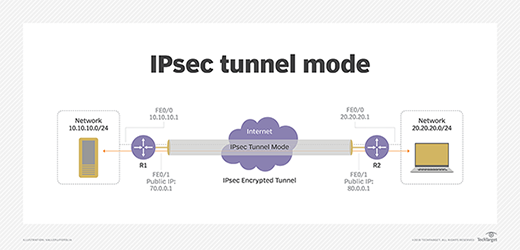
Tunnel style. Normally used between secured network gateways, IPsec tunnel manner enables hosts behind ane of the gateways to communicate securely with hosts behind the other gateway. For example, any users of systems in an enterprise branch office can deeply connect with any systems in the main office if the branch office and main function have secure gateways to deed as IPsec proxies for hosts within the respective offices. The IPsec tunnel is established between the two gateway hosts, but the tunnel itself carries traffic from any hosts inside the protected networks. Tunnel mode is useful for setting up a machinery for protecting all traffic betwixt two networks, from disparate hosts on either terminate.
Transport style. A transport mode IPsec circuit is when two hosts set up a straight continued IPsec VPN connectedness. For case, this type of circuit might be ready up to enable a remote it (Information technology) support technician to log in to a remote server to practise maintenance work. IPsec transport mode is used in cases where i host needs to interact with another host. The two hosts negotiate the IPsec excursion directly with each other, and the circuit is normally torn downward after the session is consummate.
A adjacent footstep: Comparing IPsec VPN vs. SSL VPN
A Secure Socket Layer (SSL) VPN is another approach to securing a public network connection. The 2 tin be used together or individually depending on the circumstances and security requirements.
With an IPsec VPN, IP packets are protected as they travel to and from the IPsec gateway at the edge of a individual network and remote hosts and networks. An SSL VPN protects traffic as it moves between remote users and an SSL gateway. IPsec VPNs back up all IP-based applications, while SSL VPNs just back up browser-based applications, though they can support other applications with custom development.
Acquire more about how IPsec VPNs and SSL VPNs differ in terms of authentication and access control, defending against attacks and client security. See what is best for your arrangement and where 1 type works best over the other.
This was last updated in April 2021
Continue Reading About IPsec (Net Protocol Security)
- IPsec vs. SSL VPN: Comparing speed, security risks and applied science
- SD-WAN vs. DMVPN vs. IPsec tunnels: How do I choose?
- SDP vs. VPN vs. zero-trust networks: What'due south the departure?
- What's the difference betwixt GRE and IPsec tunnels?
- Site-to-site VPN security benefits and potential risks
Dig Deeper on Network security
-

Cyberspace Key Exchange (IKE)
-

What does a VPN concentrator practice?
-

Choosing between an SSL/TLS VPN vs. IPsec VPN
-

How does BENIGNCERTAIN exploit Cisco PIX firewalls?
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchsecurity/definition/IPsec-Internet-Protocol-Security




0 Response to "When Using Ipsec, How Can You Ensure That Each Computer Uses Its Own Private Key Pair?"
Post a Comment